Context
Climate change related challenges exceed regular coping capacities of an estimated 500 million family farms. If local knowledge is not combined with modern technologies, farmers face average annual harvest reductions of up to 25% by 2050 and might lose in some years their entire harvest, as shown in the figure below.
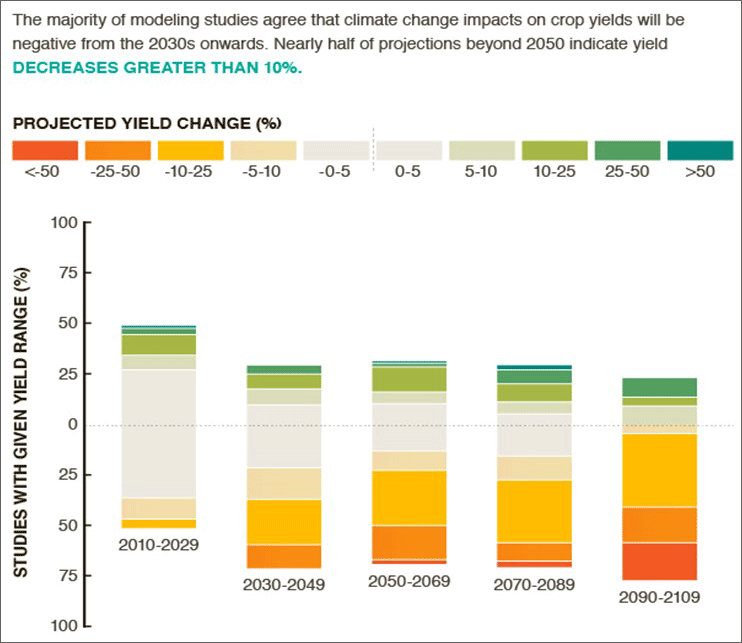
Negative impacts from climate change on crop yields largely outnumber the positive impacts from climate change by 2030 ©CGIAR
CRA is defined by the Food and Agriculture Organization (FAO), as agriculture that (1) sustainably increases productivity, (2) enhances resilience through adaptation measures and (3) reduces or removes greenhouse gases through mitigation measures. CRA is not only about plants and animals, but rather about soils, water and use of natural nutrient cycles (especially Carbon-Nitrogen-Phosphorus-Potassium C-N-P-K cycles). Implementing integrated soil management practices should thus be one of the main objective of CRA. Smallholder farmers have however important adaptation capacities since they are less stuck in a business model (which is more the case for large intensified monoculture farms).
Key elements of Climate Resilient Agriculture (CRA)
(1) Capacity (vulnerability assessment) and enabling policy and institutions; (2) Strong farmer organizations and networking; (3) Climate informed advisories and early warning; (4) Digital agriculture; (5) Climate Resilient and low emission practices and technologies (incl. smart water management interventions and modern irrigation technologies to address scarcity and enhance water productivity by adopting sustainable water resources management at basin level (water stewardship) and a landscape approach to climate and disaster resilience), (6) Prioritization and pathways of change (vulnerability integration); (7) Credit and insurance; (8) Expanded private sector activity and Public Private Partnerships (cf.
CGIAR CCAFS).
Quality criteria for CRA
In a first round of consultation, professionals from NGOs, research and donors highlighted that effective CRA approaches should contribute to 1. Productivity & ecologic resilience, 2. Adaptive capacity of stakeholders (including SDC), 3. Mitigation of greenhouse gases 4. National commitments/policies in reference to UNFCCC process (National Adaptation Plans and Nationally Determined Commitments) 5. Contributions of CRA and Food Systems to other SDGs. |
SDC’s approach
SDC is working on CRA with a systemic, collaborative, transdisciplinary and participatory approach across agriculture, food, nutritional and social services. SDC addresses the 3 main pillars of CRA (sustainably increases productivity, enhance resilience through adaptation measures, reduces or remove greenhouse gases through mitigation measures) to guide the transformation to sustainable food and agriculture systems in accordance with agroecological principles.
The “Climate Environment and Disaster Risk Reduction Integration Guidance” (CEDRIG) tool, developed by SDC links climate hazards and risks in the design of interventions and strategies in agriculture that include adaptation and mitigation in agricultural production. A+FS members may approach networks of the green cluster (CCE,
DRR,
ResEAU or Water) for
support, if a strategy is to be developed.
| Thank you to all who have co-edited this text:
Ime Ime, Thomas Kalytta, Jahangir Alam, Boris Orlowsky, Xenia Kirchhofer, Wantu Perez, Hassan Mumin Ali, Adeline Siffert, Chrons Schurr, Mohamed Salem, Boris Orlowsky, Bernard Conilh de Beyssac and Yamuna Upreti. |
Key resources
 Climate Resilient Agriculture: key points from the learning journey
Climate Resilient Agriculture: key points from the learning journey
Mélanie Surchat, SDC A&FS Network
 Climate-resilient agricultural development
Climate-resilient agricultural development
Scaling up note
IFAD, February 2015
 Towards a common food policy for the European Union
Towards a common food policy for the European Union
International Panel of Experts on Sustainable Food Systems
February 2019
 How to Feed the World in 2050
How to Feed the World in 2050
FAO, 2009
 Building climate resilience for food security and nutrition
Building climate resilience for food security and nutrition
The State of Food Security and Nutrition in the World 2018
FAO, IFAD, UNICEF, WFP and WHO
 Webinars: Coherent policies driving sustainable food systems
Webinars: Coherent policies driving sustainable food systems
16. to 20. May 2019
Organized by Helvetas, ETH and FiBL
 The Contribution of agroecological approaches to realizing climate-resilient agriculture
The Contribution of agroecological approaches to realizing climate-resilient agriculture
August 2019
Fergus Sinclair et al., August 2019
Projects
Sustainable water and pasture management to alleviate the plight of pastoralists (Ethiopia)
SDC takes measures to improve food security of pastoralists and their resilience to crisis situations, for example through the rehabilitation of pastureland and water points or the introduction of land use plans.
Overview of context and aim
Solar Irrigation for Agriculture Resilience (South Asia)
The project aims to address the challenges arising from increased irrigation (depleting groundwater resources and raising energy demand) by promoting solar irrigation, water efficient agriculture and groundwater governance.
Overview of context and aim
Programa de Reduccion de Riesgo de Desastres (Bolivia)
The SDC project intended to develop a lasting/sustainable culture of resilience among public sector with training of key agents of change and raising awareness among population.
Overview of context and aim
Program for sustainable production in the cacao sector (Indonesia)
This public private partnership program aims to increase competitiveness of an environmentally responsible and inclusive cocoa value chain through capacity building of smallholder farmers
Overview of context and aim
Closing rice yield gaps (China, Indonesia, Myanmar, Sri Lanka, Thailand, and Vietnam)
SDC supports IRRI and its national research and extension partners to develop tools and methods to increase the productivity, resource-use efficiency, and sustainability of irrigated rice production systems
Overview of context and aim
Transforming the Charcoal Sector (Tanzania)
The project formalized, up-scaled and promoted a tested and functioning model of a sustainable, more energy efficient charcoal value chain using a Community Based Forest Management approach
Overview of context and aim
Innovation and dissemination of technologies for adaptation of agriculture to climate change (Nicaragua)
The project provides resources so that small-holder farmers in environmentally degraded dry areas affected by climate change develop capacities, exchange knowledge and apply technologies for climate change adaptation
Overview of context and aim
World Overview of Conservation Approaches and Technologies (WOCAT)
The project supported this Global Sustainable Land Management Platform, focusing mainly on enhancement of knowledge uptake in decision support
Overview of context and aim
WOCAT Climate Change Adaptation module
Community
07 October 2021
Building disaster resilience by up-scaling African Risk Capacity’s insurance coverage
Presentations on ARC workshop and ARC regional achievements are now available online
19 Janvier 2021
E-atelier sur CEDRIG
organisé par le réseau A&FS pour le personnel de la DDC en Afrique de l'Ouest
25 February 2020
E-workshop on the climate proofing tool CEDRIG
organised by
the SDC Agriculture & Food Security Network for SDC staff in East Africa
19 November to 6 December 2018 t
Online dialog and webinar series on climate resilient agriculture
organised by the SDC Agriculture & Food Security Network - together with thematically related SDC Networks