The following examples illustrate some of the results that UNDP has achieved in the areas listed above:
Reducing human poverty through sustainable development pathways
UNDP fights poverty with knowledge. It provides countries with evidence-based policy advice, as well as with the connections and know-how to access and manage resources in a sustainable way.
In 2014, UNDP projects helped 11.2 million people in 94 countries to improve their livelihoods. This happened by creating new jobs, fostering adaptation to the effects of climate change, protecting biodiversity, and by providing technical support. In rural Mali, for example, a UNDP-backed project is helping families to install solar panels on their own homes, where they are used to produce power to boil water for cooking and run pumps for vegetable gardens. Beneficiaries also have inside electric lighting for the first time in their lives.
In 2014, UNDP further supported 57 countries in integrating biodiversity and ecosystem management into development planning. As an example, in Afghanistan UNDP helped to establish 279 rural infrastructure projects in energy, transport, water supply, natural resources, disaster management, and agriculture, benefiting 2.8 million people.
Building and strengthening inclusive and effective democratic governance
UNDP plays a key role in strengthening democratic governance around the world. It supports democratic systems in becoming more inclusive, accountable, and able to meet expectations with regard to participation, services and security. In 2014, UNDP programmes supported electoral processes around the world and helped register 18 million new voters.
UNDP also works to strengthen national parliaments, assists dozens of countries with legal reform, helps improve judicial systems, and is an advocate for human rights.
In Bangladesh, for example, UNDP has worked with local authorities and legal assistance groups to help indigenous peoples gain fairer representation in the courts. Another example of UNDP's work is its engagement in the fight against corruption. In the Arab region, UNDP has helped to develop, implement and monitor national anti-corruption strategies. In 23 countries, UNDP has further strengthened the capacity of institutions to fulfil human rights obligations. In Burkina Faso, for example, a law was adopted to prevent and punish torture and similar practices.
To ensure universal access to basic services and to fight against discrimination, UNDP is also active in supporting populations affected by HIV. In 2014, for instance, UNDP contributions resulted in HIV-related law reviews and reforms in Lesotho, Namibia, Swaziland and Tanzania.
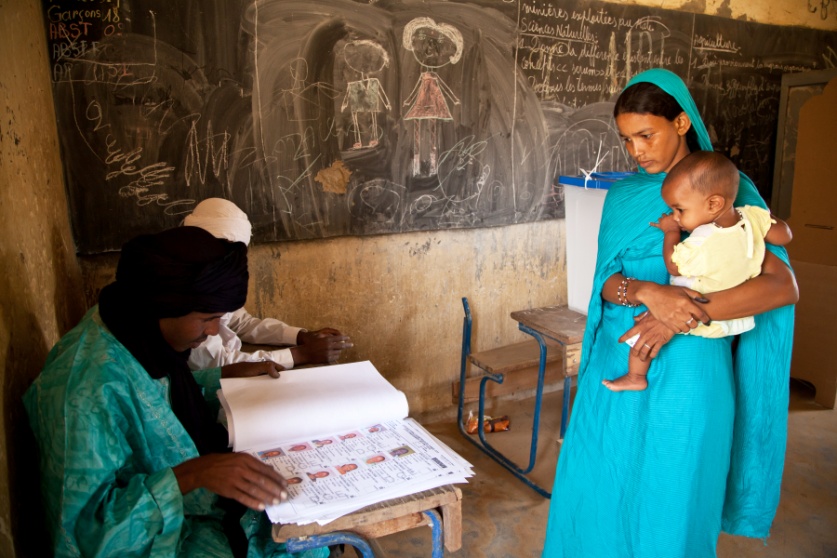

Building resilience through support for crisis prevention and recovery
UNDP assists countries in reducing the risk of armed conflict and potential damage from natural disasters. When crises occur, it supports affected societies with mitigation measures, and provides a link between immediate response and long-term recovery.
During 2014, UNDP projects led to 98 new disaster reduction and adaption plans being put in place in 23 countries. Many of them take into account that women and men are not always affected by disasters in the same way. The plans are therefore designed in a gender-responsive way. In 20 conflict-affected countries, UNDP helped to restore livelihoods and create jobs. In Syria for example, UNDP supported small business, resulting in more than 18 000 new jobs and the restoration of basic public infrastructures.
Coordination of the United Nations development system
In 2014, UNDP continued to pay close attention to its responsibilities and leadership role in the United Nations development system. It engaged with UN partners to develop a common vision for United Nations system readiness to deliver on the Sustainable Development agenda. As a Resident Coordinator and System Manager, UNDP continued to ensure that the system is mutually accountable and collectively owned. By participating in 44 "Delivering as One" initiatives, UNDP further helped to reduce transaction costs and duplication of efforts, in addition to enhancing cost-effectiveness.
Picture
A woman at the ballot box in a school during the 2013 Mali presidential elections (© UN/Blagoje Grujic)